Introduction
Obesity is a global epidemic that significantly increases the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and certain cancers. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), worldwide obesity rates have nearly tripled since 1975, with over 1.9 billion adults classified as overweight, and more than 650 million considered obese in 2022. In the United States, obesity affects approximately 42.4% of adults, leading to a significant public health burden (CDC, 2023).
Understanding Obesity
Obesity is defined as an excessive accumulation of body fat, usually measured using the Body Mass Index (BMI):
- Normal Weight: BMI of 18.5–24.9
- Overweight: BMI of 25–29.9
- Obese: BMI of 30 or higher
- Severely Obese: BMI of 40 or higher
Causes and Risk Factors
- Poor Diet: High-calorie intake, excessive sugar and fat consumption.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles contribute to weight gain.
- Genetic Factors: Family history can influence metabolism and fat storage.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions such as hypothyroidism and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) affect weight regulation.
- Environmental and Psychological Factors: Stress, poor sleep, and socioeconomic factors play a role.
Signs & Symptoms of Obesity
- Excessive Weight Gain: Increased fat accumulation, particularly around the abdomen.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing with minimal activity due to increased body mass.
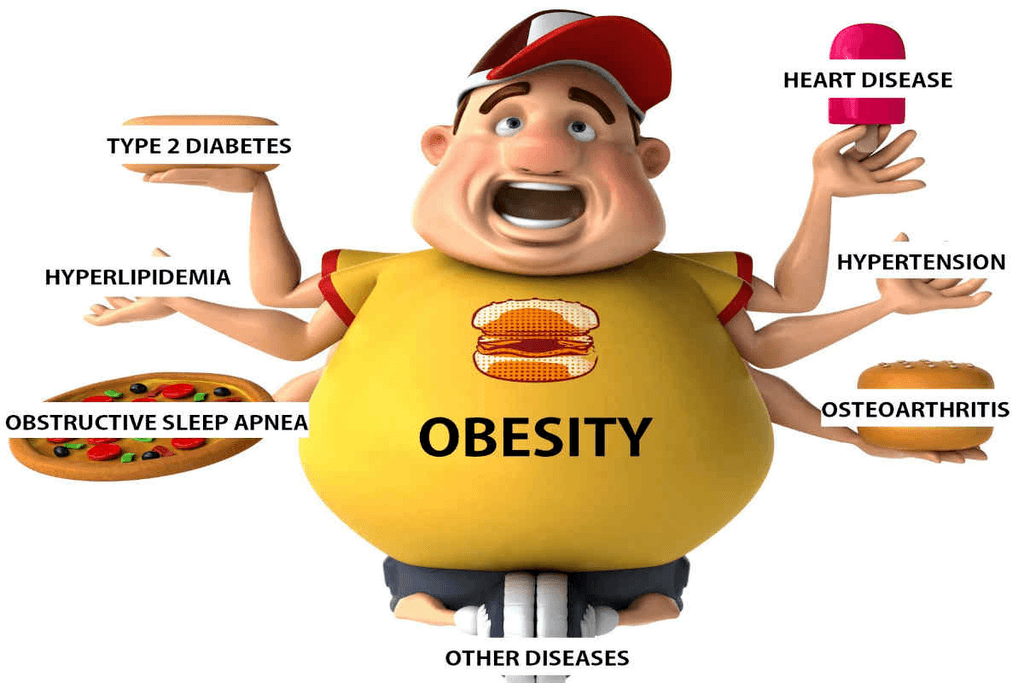
- Joint Pain: Excessive weight places stress on bones and joints, leading to osteoarthritis.
- Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases: Higher likelihood of developing diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease.
- Low Energy Levels: Fatigue and reduced stamina due to metabolic imbalances.
Health Complications Related to Obesity
- Type 2 Diabetes: Excess fat leads to insulin resistance, increasing blood sugar levels.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Obesity contributes to hypertension, high cholesterol, and atherosclerosis.
- Stroke: Higher risk due to elevated blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Liver Disease: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is common in obese individuals.
- Sleep Apnea: Excess fat around the neck can obstruct breathing during sleep.
- Certain Cancers: Increased risk of colorectal, breast, and endometrial cancers.
- Mental Health Disorders: Higher rates of depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
Prevention and Precautionary Measures
- Adopt a Balanced Diet: Increase intake of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Engage in Daily Physical Activity: At least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
- Avoid Processed and Fast Foods: Reduce consumption of sugary drinks, refined carbohydrates, and trans fats.
- Monitor BMI Regularly: Maintain a healthy weight through consistent tracking.
- Prioritize Mental Health: Manage stress, seek counseling, and ensure proper sleep hygiene.
Treatment and Cure for Obesity
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Caloric restriction and portion control.
- Regular physical exercise.
- Behavioral therapy and dietary counseling.
2. Medical Interventions
- Medications: FDA-approved weight-loss drugs such as Orlistat, Semaglutide, and Phentermine.
- Bariatric Surgery: For severe obesity (BMI >40), procedures like gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy can be effective.
- Hormonal Therapy: Emerging treatments targeting metabolic regulation.
3. Emerging Research and Innovations
- Gut Microbiome Studies: Research shows gut bacteria influence obesity risk (Harvard Medical School, 2023).
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Medications like Semaglutide improve weight loss by regulating appetite (New England Journal of Medicine, 2023).
- Gene Therapy: Investigating genetic factors that influence obesity susceptibility (NIH, 2023).
Conclusion
Obesity is a preventable and manageable condition that requires a multifaceted approach. Through lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and ongoing research, individuals can reduce their risk of obesity-related diseases. Raising awareness and promoting healthier habits remain key strategies in addressing the global obesity epidemic.
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). (2023). Global Obesity Trends.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2023). U.S. Obesity Statistics.
- Harvard Medical School. (2023). The Role of Gut Microbiota in Obesity.
- New England Journal of Medicine. (2023). Advances in Obesity Treatment.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2023). Genetic Factors in Obesity.