Tuberculosis (TB), a bacterial infection primarily affecting the lungs, has seen a notable resurgence in the United States. In 2024, over 10,300 cases were reported, marking an 8% increase from the previous year and reaching the highest levels since 2011. AP News+1CDC+1
State-by-State Breakdown of TB Cases
The rise in TB cases has been observed across various states, with 34 states and the District of Columbia reporting increases from 2023 to 2024. CDC
Causes and Transmission of Tuberculosis
TB is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It spreads through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or speaks, releasing microscopic droplets containing the bacteria. Inhaling these droplets can lead to infection. While TB primarily affects the lungs, it can also impact other parts of the body, such as the kidneys, spine, and brain. CDC
A Brief History of Tuberculosis
TB has afflicted humans for millennia, with evidence of the disease found in Neolithic human remains dating back approximately 9,000 years. Historically known as “consumption,” TB was a leading cause of death in the 18th and 19th centuries. The discovery of the TB-causing bacterium by Robert Koch in 1882 paved the way for better understanding and treatment of the disease. Encyclopedia Britannica
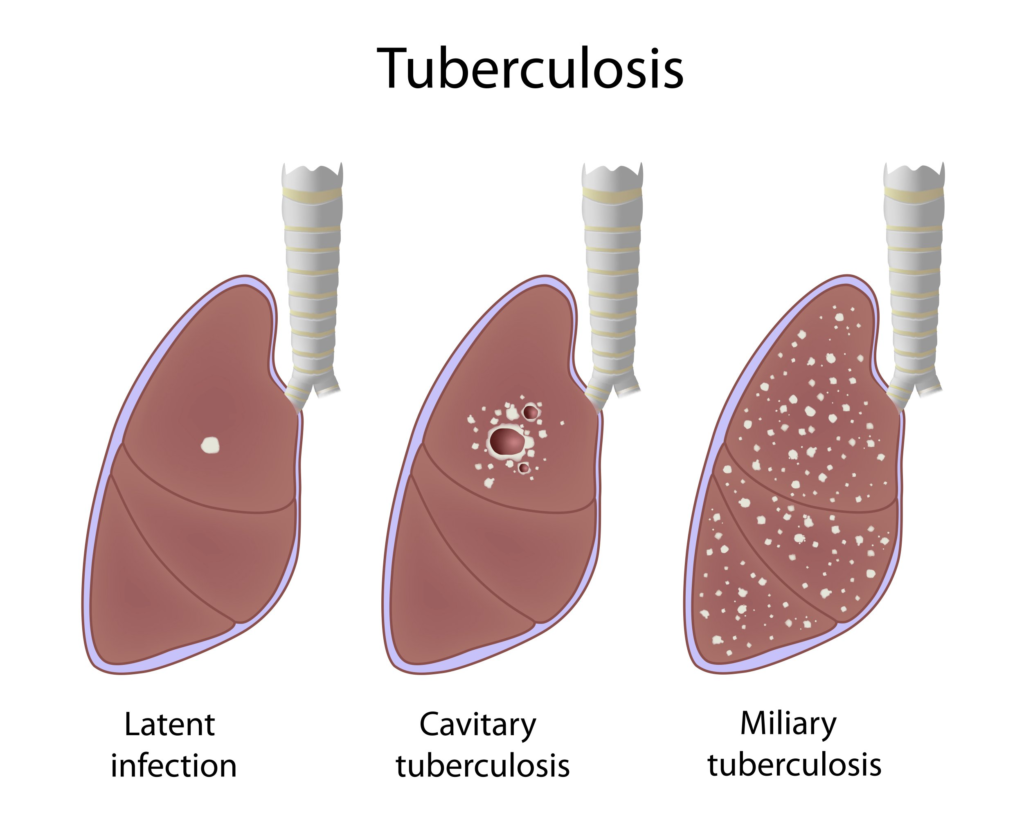
The Importance of Vaccination
The Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine has been used for nearly a century to protect against TB. While it offers moderate protection against severe forms of TB in children, its efficacy in adults varies. In the United States, the BCG vaccine is not widely administered due to the relatively low risk of TB infection and the vaccine’s variable effectiveness. However, in countries with high TB prevalence, vaccination remains a crucial preventive measure. Gates Foundation
Preventive Measures for the General Population
To mitigate the risk of contracting TB, individuals should:
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing and covering the mouth when coughing or sneezing can reduce the spread of respiratory infections.
- Ensure Proper Ventilation: Well-ventilated living and working spaces decrease the concentration of airborne bacteria.
- Seek Medical Attention Promptly: Early detection and treatment of TB are vital. Symptoms include a persistent cough lasting more than three weeks, chest pain, and coughing up blood.
- Complete Prescribed Treatments: Adhering to the full course of TB medication prevents the development of drug-resistant strains.
- Support Public Health Initiatives: Participate in TB screening programs and stay informed about local TB outbreaks.
Conclusion
The recent increase in TB cases in the United States underscores the need for public awareness and proactive preventive measures. By understanding the causes, history, and importance of vaccination, and by adopting recommended precautions, we can work collectively to curb the spread of this enduring disease.
Recent Surge in Tuberculosis Cases Across the United States
Tuberculosis cases in the US rose to their highest levels in more than a dozen years
3 days agoAP NewsThe tuberculosis outbreak in Kansas is alarming. It’s not the biggest in US history though, CDC says55 days ago
Sources