Introduction
Neurological disorders affect millions of people worldwide, impacting cognitive function, motor skills, and overall quality of life. Among the most prevalent conditions are Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke. These disorders have significant social and economic consequences, with rising prevalence rates due to aging populations.
Global Statistics:
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Over 55 million people worldwide are living with dementia, with Alzheimer’s being the most common form (WHO, 2023).
- Parkinson’s Disease: Affects more than 10 million people globally, with cases expected to double by 2040 (Parkinson’s Foundation, 2023).
- Stroke: Responsible for one in six deaths globally, with over 12 million strokes occurring each year (World Stroke Organization, 2023).
Understanding these conditions, their warning signs, risk factors, and prevention strategies is essential for early intervention and effective management.
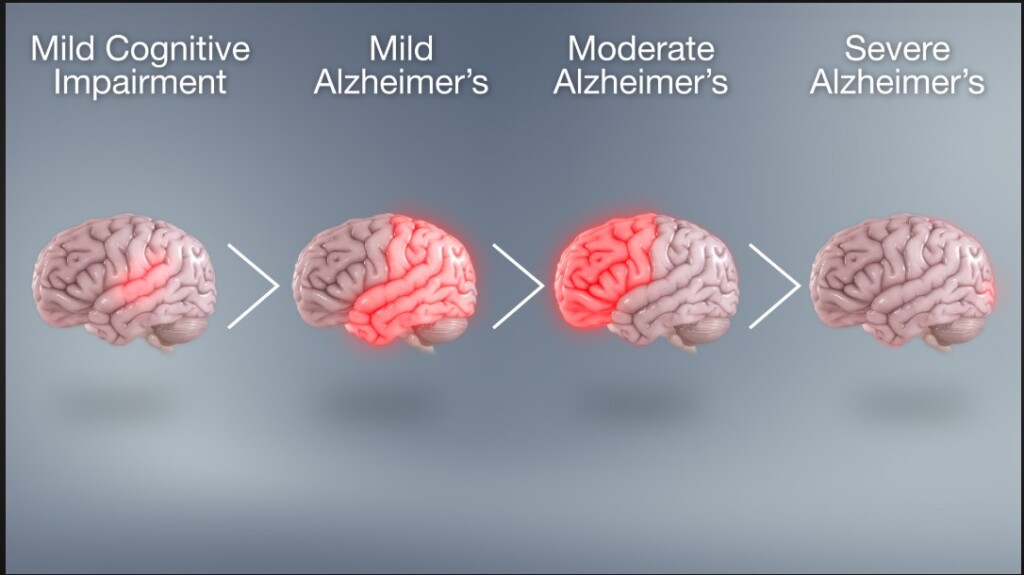
1. Alzheimer’s Disease
Overview:
Alzheimer’s is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that leads to memory loss, cognitive decline, and changes in behavior. It primarily affects older adults.
Signs & Symptoms:
- Memory loss and confusion
- Difficulty solving problems or planning
- Trouble recognizing familiar places or people
- Mood swings and personality changes
- Difficulty speaking or writing
Risk Factors:
- Age (most common in those over 65)
- Family history and genetics (APOE-e4 gene increases risk)
- Head injuries and brain trauma
- Cardiovascular diseases (high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity)
Precaution & Prevention:
- Brain-Healthy Diet: Mediterranean and DASH diets, rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Cognitive Stimulation: Reading, puzzles, learning new skills to maintain mental agility.
- Social Engagement: Staying connected with friends and family reduces cognitive decline.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise improves blood flow to the brain and reduces inflammation.
Treatment & Cure:
- No cure exists, but FDA-approved drugs like Aducanumab (Aduhelm) and Lecanemab (Leqembi) slow disease progression.
- Lifestyle modifications and therapies (cognitive behavioral therapy, music therapy) can help manage symptoms.
- Ongoing research focuses on new immunotherapies and gene-targeted treatments.
2. Parkinson’s Disease
Overview:
Parkinson’s is a progressive disorder affecting movement and motor control due to dopamine-producing neuron degeneration.
Signs & Symptoms:
- Tremors (shaking hands, fingers, or chin)
- Muscle stiffness and rigidity
- Slowed movements (bradykinesia)
- Balance problems and frequent falls
- Speech changes and difficulty swallowing
Risk Factors:
- Age (most common after 60 but can develop earlier)
- Genetic predisposition
- Exposure to toxins (pesticides, heavy metals)
- Head injuries
Precaution & Prevention:
- Regular Exercise: Activities like Tai Chi and yoga improve balance and flexibility.
- Healthy Diet: Antioxidant-rich foods help protect brain cells.
- Avoid Toxins: Minimize exposure to pesticides and industrial chemicals.
- Early Screening: Genetic and biomarker testing for at-risk individuals.
Treatment & Cure:
- Medications: Levodopa (L-Dopa), Dopamine Agonists (Pramipexole), and MAO-B inhibitors slow progression.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): Implanted electrodes can improve motor symptoms.
- Emerging Therapies: Gene therapy and stem cell research are advancing treatment options.
3. Stroke
Overview:
A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, leading to brain cell death. It is a leading cause of disability and death worldwide.
Signs & Symptoms:
- F.A.S.T. Warning Signs:
- Face drooping
- Arm weakness
- Speech difficulty
- Time to call emergency services
- Sudden numbness in the limbs
- Severe headaches with no known cause
- Difficulty walking, dizziness, or loss of coordination
Risk Factors:
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Diabetes and obesity
- High cholesterol
- Sedentary lifestyle
Precaution & Prevention:
- Blood Pressure Control: Maintain normal levels through diet and medication.
- Healthy Diet: Reduce salt, saturated fats, and cholesterol intake.
- Regular Exercise: At least 150 minutes of moderate activity per week.
- Manage Diabetes: Keep blood sugar levels in check to prevent vascular damage.
Treatment & Cure:
- Emergency Stroke Treatments: Clot-busting drugs (tPA) administered within 4.5 hours of symptoms can minimize brain damage.
- Surgical Interventions: Thrombectomy procedures remove large blood clots.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy help restore function.
- Preventative Medications: Blood thinners and cholesterol-lowering drugs reduce the risk of recurrence.
Conclusion
Neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and stroke significantly impact individuals and societies worldwide. Although cures remain elusive, early detection, lifestyle modifications, and innovative treatments provide hope for better management and quality of life. With continued research and public awareness, these conditions can be better understood and addressed.
References:
- World Health Organization (WHO). (2023). Neurological Diseases Global Reports.
- Alzheimer’s Association. (2023). Facts and Figures on Dementia and Alzheimer’s.
- Parkinson’s Foundation. (2023). Global Prevalence and Treatment Advancements.
- World Stroke Organization. (2023). Stroke Prevention and Recovery.
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). (2023). Recent Advances in Neurological Research.